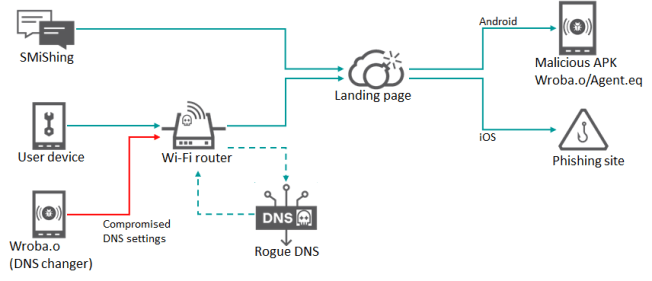
Roaming Mantis threat actors were observed using a new variant of their mobile malware Wroba to hijack DNS settings of Wi-Fi routers.
Researchers from Kaspersky observed Roaming Mantis threat actors using an updated variant of their mobile malware Wroba to compromise Wi-Fi routers and hijack DNS settings.
Roaming Mantis surfaced in March 2018 when hacked routers in Japan to redirect users to compromised websites. Roaming Mantis is a credential theft and malware campaign that leverages smishing to distribute malicious Android apps in the format of APK files.
Investigation by Kaspersky Lab in 2018 indicates that the attack targeted users in Asia with fake websites customized for English, Korean, Simplified Chinese, and Japanese. Most of the impacted users were in Bangladesh, Japan, and South Korea.
Over the years, the threat actors targeted users worldwide, including Russia, India, Bangladesh, Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan, Iran, Vietnam, and Europe.
In September 2022, Kaspersky researchers analyzed the new Wroba variant and discovered that it was designed to target specific Wi-Fi routers mainly used in South Korea.
“Kaspersky has been investigating the actor’s activity throughout 2022, and we observed a DNS changer function used for getting into Wi-Fi routers and undertaking DNS hijacking. This was newly implemented in the known Android malware Wroba.o/Agent.eq (a.k.a Moqhao, XLoader), which was the main malware used in this campaign.” reads the report published by Kaspersky.
The DNS changer implemented in the new version connects to the hardcoded vk.com account “id728588947” to get the next destination (107.148.162[.]237:26333/sever.ini)”. The “sever.ini” (note the misspelling of server) is dynamically provided the threat actors’ DNS IP addresses.
“Checking the code of the DNS changer, it seems to be using a default admin ID and password such as “admin:admin”. Finally, the DNS changer generates a URL query with the rogue DNS IPs to compromise the DNS settings of the Wi-Fi router, depending on the model” continues the report.
Roaming Mantis threat actors can use the new DNS changer functions to manage all communications from devices using a compromised Wi-Fi router. An attacker can redirect to malicious web pages and interfere with security product updates.
The experts illustrated an attack scenario in which users connect infected Android devices to free/public Wi-Fi. Connecting the infected device to a targeted Wi-Fi model with vulnerable settings, the Wroba Android malware will compromise the router and will target other devices.
“Users with infected Android devices that connect to free or public Wi-Fi networks may spread the malware to other devices on the network if the Wi-Fi network they are connected to is vulnerable.” concludes the report. “Kaspersky experts are concerned about the potential for the DNS changer to be used to target other regions and cause significant issues.”
Follow me on Twitter: @securityaffairs and Facebook and Mastodon
| [adrotate banner=”9″] | [adrotate banner=”12″] |
(SecurityAffairs – hacking, Roaming Mantis)
[adrotate banner=”5″]
[adrotate banner=”13″]
The post Roaming Mantis uses new DNS changer in its Wroba mobile malware appeared first on Security Affairs.